kW v kWH
What is the difference between a kilowatt and kilowatt hour? We explain the difference and when to use each one.
- kW (kilowatt) refers to power and is used when talking about the output speed of EV chargers
- kWh (kilowatt hour) is a unit of energy and is used when talking about electric car battery capacity and the ‘amount’ of energy put into the battery from the charger.
With so many different acronyms floating around when it comes to electric cars (BEV, PHEV, RFID, CCS – the list goes on!) it can start to get overwhelming. Here at Osprey, we want to make electric as easy as possible so have broken down the difference between kilowatts (kW) and kilowatt hours (kWh) and when to use each one.
What is the difference between kWs and kWhs?
At Osprey, our rapid EV charging is priced in kWh (kilowatt hours) of energy delivered to your car. Think of kWh as the electric equivalent to litres of fuel. A petrol or diesel car has a fuel tank that can store so many litres of fuel; an electric car has a battery that can store so many kWh. That’s pretty simple right?
So then what is a kilowatt?
A kilowatt refers to how much power a charger has in order to deliver the energy – essentially how quickly the charger can transfer energy to the car. The higher the kW power rating on a rapid charger, the faster the output of the charger to deliver the kWh.
A 150kW rapid charger delivers electricity twice as fast as a 75kW rapid charger because it is twice as powerful. To determine the actual amount of electricity delivered there needs to be a period of time over which that rate occurs. This is where a kWh comes in. One kWh is the same as electricity delivered at a rate of 1kW for a period of one hour.
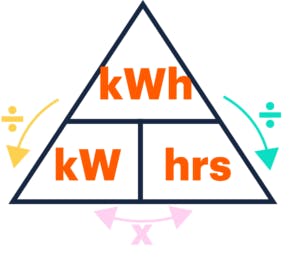
The relationship between kilowatt-hours, kilowatts and time.
Here’s how it works in the real world.
A 75kW charger has the ability, or power, to deliver up to 75kWh in the space of one hour, or 1.25kWh every minute. A 150kW charger can deliver up to 150kWh in an hour, or 2.5kWh every minute. Once the charger is connected to your car, the energy itself (now measured in kWh) is transferred to your car.
It is important to note that while a 75kW charger has the ability to deliver 75kWh in one hour, there are many things that will affect the actual charge rate, including your car’s maximum charging rate. Read more about charge rates here.
Your electric vehicle’s battery stores electricity in kWh, and as you drive the kWh get used up. When using our EV chargers, you will be billed for the kWh you put into your car, much like at the fuel pump where you are charged for litres. And with filling a fuel tank with petrol or diesel, the amount of kWh delivered will vary from car to car and charging session to charging session.
When you think about it in terms of petrol or diesel cars, it is all pretty straightforward. When you plug into an electric car charger the energy (fuel) you take to fill up your battery (fuel tank) is measured in kWh (litres). The speed in which you can get that energy (fuel) is determined by the power (measured in kW) of the EV charger.
Charge with us.
Driving and re-charging an electric vehicle is a new experience and can seem daunting when you first set out. Discover simple and rapid re-fuelling on the Osprey network.





